In this section, you will:
- Remotely access an imported Amazon EKS cluster using the Rafay integrated browser based Zero Trust Kubectl
- View Kubectl audit logs
Estimated Time
Estimated time burden for this part is 5 minutes.
Step 1: Zero Trust Kubectl
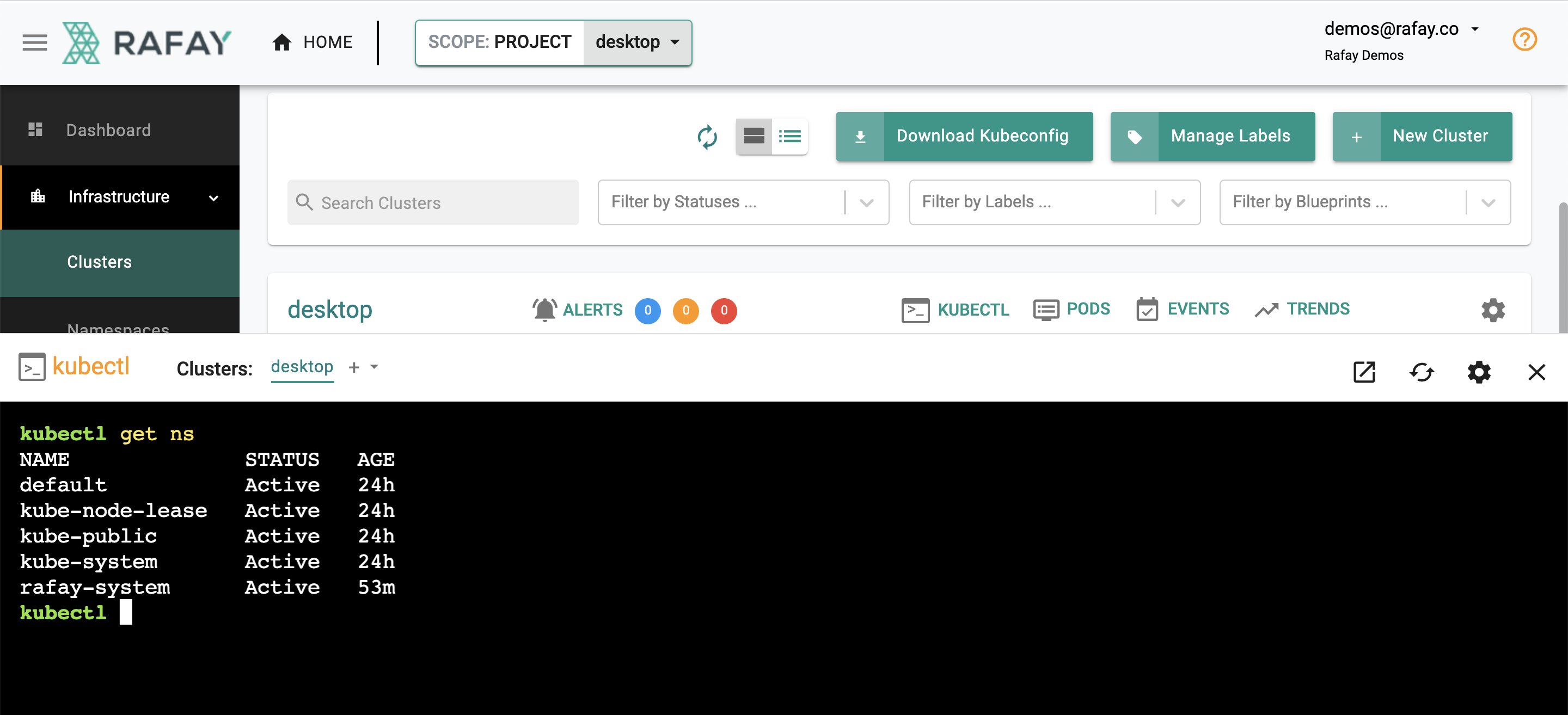
- Navigate to your aws-workshop project and Infrastructure -> Clusters
- Click on the Kubectl link on the imported cluster. This will provide you with a web based, zero trust kubectl shell.
- Type in a kubectl command such as
kubectl get nsto get a response from the remote cluster on your desktop operating behind a NAT/firewall.
The controller injects a service account (sa) Just In Time(JIT) on the target cluster. The service account is automatically configured with the user’s role in the Org. You can view the JIT service account by using the following command. In the example below, the service account for the user demos@rafay.co was created just 5 seconds back as the user opened the web based kubectl console. The service account is automatically removed from the target cluster once the configured lifetime expires.
kubectl get sa -n rafay-system
NAME SECRETS AGE
default 1 53m
demos-64rafay-46co 1 5s
system-sa 1 53mStep 2: Audit Logs
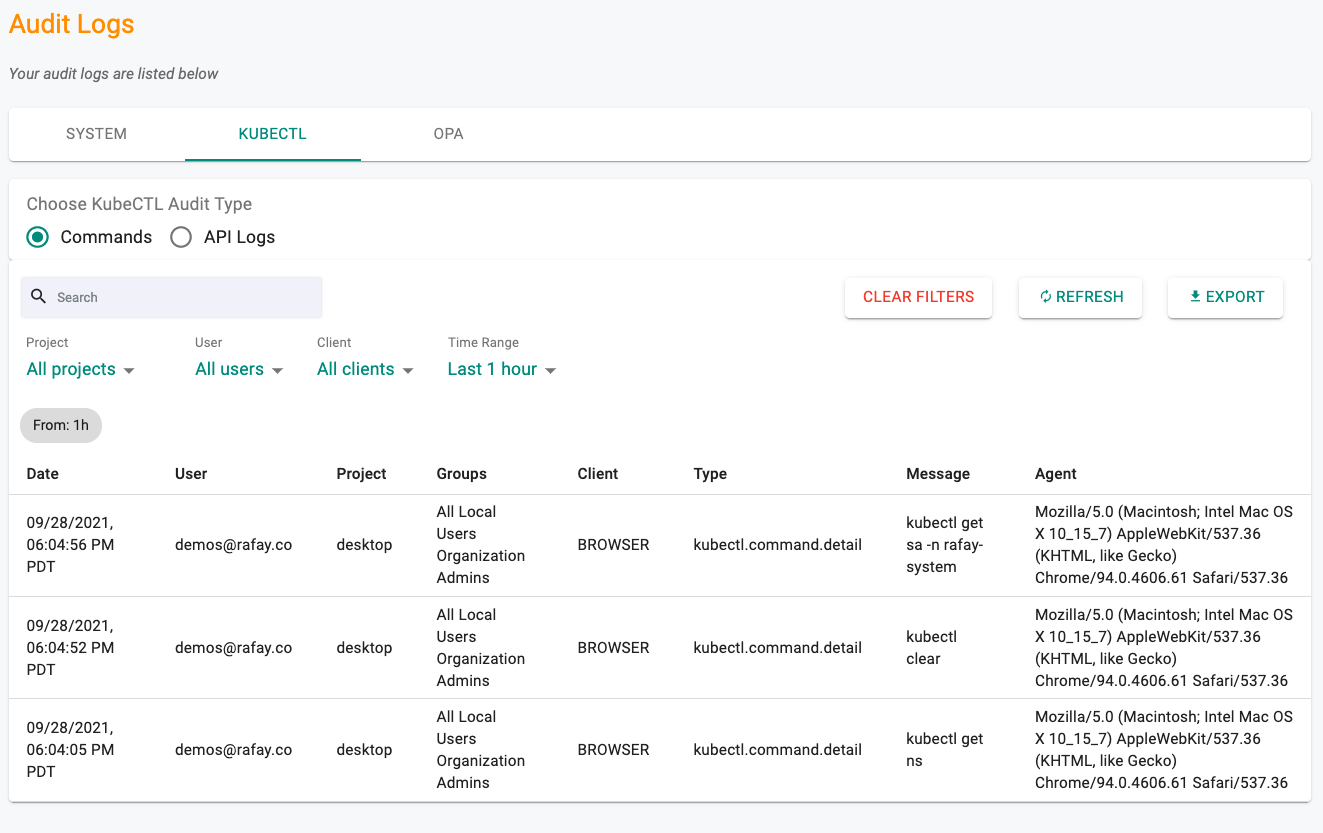
All commands performed using the zero trust kubectl channel are centralized through the controller. As a result, a complete audit trail of “who did what and when” is maintained. Administrators can view these audit logs.
- Click on Home -> System -> Audit Logs
- Click on the Kubectl tab
Audit logs can be viewed by API or Commands (for web based shell). See an example of the audit logs below.
Recap
Congratulations! In this part, you
- Experienced how remote users can securely access kubernetes clusters behind firewalls using zero trust kubectl
- Viewed the centralized audit logs for all kubectl based commands performed by users on managed clusters.